News



HPE BlueHorizon
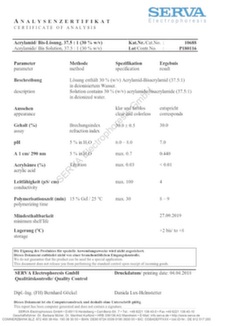
Certificates of Analysis now online!

SERVA Serving Scientists





When subscribing to »SERVA InfoMail« you will receive information about the latest product release, special promotions, new jobs at SERVA and more. This service is, of course, free of charge.
You may remove your name any time from the list of recipients.
Using the Quick Order field, you can add a product to your shopping cart with just one click. All you have to do: enter the Cat.No. as shown in our catalog in the format xxxxx.yy and click the Go!-Button.